
Anti-BrdU Antibodies — Reliably Measuring Cell Proliferation
BrdU (5’-bromo-2’-deoxyuridine) cell proliferation assay is a mainstream technique for studying cell proliferation and has been used since the 1980s (Miller and Nowakowski 1988). In actively dividing cells, BrdU, a thymidine analog, is incorporated into newly synthesized DNA instead of thymidine. Incorporated BrdU can then be detected using a specific antibody, thereby identifying dividing cells. The technique has many advantages including its low cost and the lack of radioactivity or toxicity of BrdU, when used at low concentrations (Crane and Bhattacharya 2013).
The key to a successful BrdU staining experiment is to find the most specific and suitable anti-BrdU antibody. However, this can be challenging.
Bio-Rad BrdU Antibodies
At Bio-Rad, we understand the importance of antibody validation and guarantee that the antibodies you purchase are specific and generate reproducible results. Bio-Rad’s premium PrecisionAb label, is reserved for antibodies that meet stringent performance criteria within our validation program to give you complete confidence in the antibodies you use.
Bio-Rad's range of PrecisionAb Anti-BrdU Antibodies can be used for various applications including fluorescent immunocytochemistry (Figure 1) and flow cytometry (Figure 2).
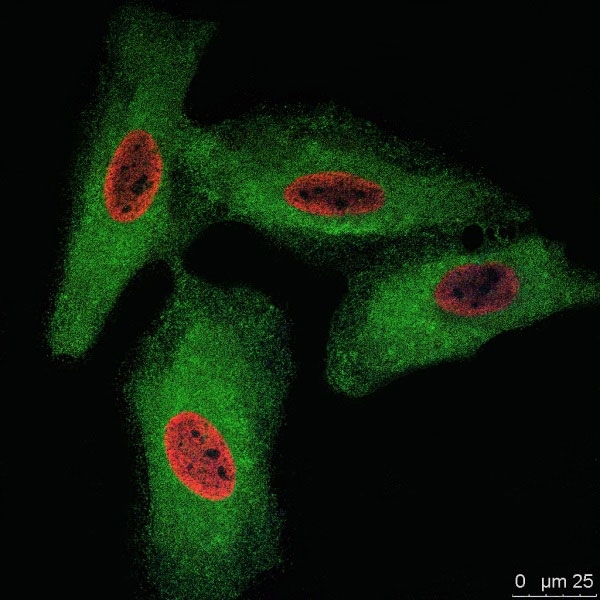
Fig. 1. HeLa cells were treated with BrdU and stained with Rat Anti-BrdU Antibody (MCA6144).
Steps taken to demonstrate the antibody specificity:
- Each antibody is quality control tested in its recommended application
- Protocols for specific antibodies in specific applications are provided
- Antibodies are tested for cross-reactivity with thymidine and other thymidine analogs
- Each antibody comes with in-depth information including details of the immunogen used in its generation
- Stringent batch-to-batch quality control
In our anti-BrdU range of antibodies we also offer recombinant anti-BrdU antibodies.
Added benefits of the recombinant anti-BrdU antibody range:
- Antibodies are sequenced, ensuring long-term security of supply
- Unlike traditional methods to generate antibodies, no immunisation of animals is involved
- Rabbit and rat isotypes are available
- Antibodies are selected using the RapMAT® Rapid Pool Affinity Maturation
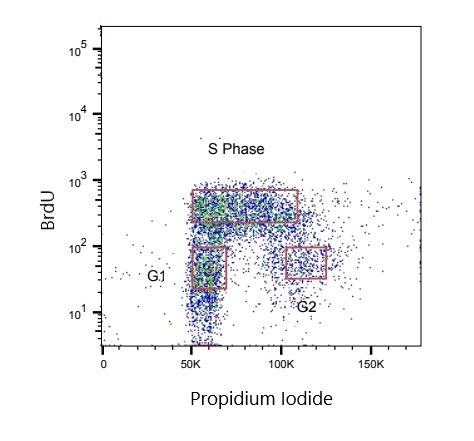
Fig. 2. Jurkat cells were treated with 100 µM BrdU and stained with Human Anti-BrdU Antibody (HCA322). Propidium iodide was used to stain total DNA.
For accurate, reliable, and trustworthy data, try PrecisionAb Anti-BrdU Antibodies .
Recent Additions To Our Range:
- PrecisionAb Rat Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone RF04-2 (MCA6143)
- PrecisionAb Rat Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone RF06 (MCA6144)
- PrecisionAb Recombinant Human Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AbD33758kg (HCA320)
- PrecisionAb Human Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AbD33761kd (HCA321)
- PrecisionAb Human Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AbD33758kd (HCA322)
- PrecisionAb Human Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AbD33761kd (HCA323)
Related Topics
alamarBlue Cell Proliferation and Viability Reagent
MCM2 Proliferation Detection Antibody
References
Crane A and Bhattacharya SK (2013). The use of bromodeoxyuridine incorporation assays to assess corneal stem cell proliferation. Methods Mol Biol 1,014, 65–70.
Miller M and Nowakowski R (1988). Use of bromodeoxyuridine-immunohistochemistry to examine the proliferation, migration and time of origin of cells in the central nervous system. Brain Res 457, 44–52. RapMAT is a trademark of MorphoSys AG.
